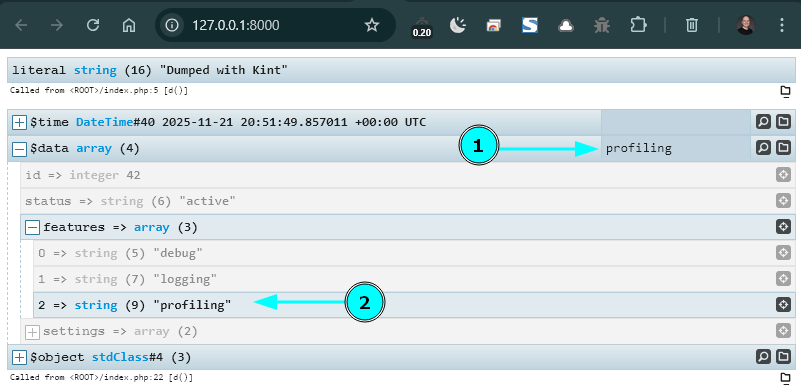
Here’s a clean, American-blog-style rewrite:
Setting up Xdebug isn’t always straightforward. Depending on your setup, you might need to wire it into your IDE or get it running inside a Docker container.
So in this tutorial, we’ll walk through a simple, foolproof way to set up Xdebug on Ubuntu Linux.
Instalation
First of all, check your PHP version with php -v.
php -v
PHP 8.4.15 (cli) (built: Nov 20 2025 17:43:25) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Built by Debian
Zend Engine v4.4.15, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.4.15, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
with Xdebug v3.4.7, Copyright (c) 2002-2025, by Derick RethansOndřej Surý’s PPA
Now, if you installed PHP from Ondřej Surý’s repository, which is always the most up-to-date, you can install xdebug with.
Note that you need to change your xdebug version to match your PHP version.
sudo apt-get install php8.4-xdebugDefault PPA
But, if you are using the standard version of PHP included with Ubuntu, which is usually outdated, simply run:
sudo apt-get install php-xdebugRun the php -v again and you should see the Xdebug information on the last line:
php -v
PHP 8.4.15 (cli) (built: Nov 20 2025 17:43:25) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Built by Debian
Zend Engine v4.4.15, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.4.15, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
with Xdebug v3.4.7, Copyright (c) 2002-2025, by Derick RethansThen, run the built-in web server and you will also see a warning:
php -S 127.0.0.1:8000
[Sat Nov 22 12:00:22 2025] PHP Warning: JIT is incompatible with third party extensions that override zend_execute_ex(). JIT disabled. in Unknown on line 0
[Sat Nov 22 12:00:22 2025] PHP 8.4.15 Development Server (http://127.0.0.1:8000) startedThis warning is normal when you’re using Xdebug on PHP 8.1+ (including 8.4).
Nothing is broken… So, what this warning means?
Xdebug overrides the internal zend_execute_ex()function, which the PHP Just-In-Time compiler (JIT) also needs, since both can’t run at the same time, PHP automatically disables JIT.
This scenario, with no JIT and using Xdebug, is generally satisfactory for a development environment.
Usage
Step Debugging
Xdebug’s step debugger allows you to interactively walk through your code to debug control flow and examine data structures.
Configuring Step Debugging
On the linux shell, run the command below to find the current php.ini file.
php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File"Output: Loaded Configuration File => /etc/php/8.4/cli/php.ini
Then, change (or include) the setting to xdebug.mode=debug, in case of inclusion, you can put it at the bottom of the file.
In setups where PHP/Xdebug and your IDE all run on the same host, this is all you need to configure on the PHP and Xdebug side.
Command Line Debug Client
The command line debug client allows you to debug PHP scripts without having to set up an IDE. This might be useful if you don’t want to tie your xdebug to a specific IDE.
A binary for Linux, macOS, and Windows is available on the Xdebug downloads page. Here I will use Linux (x86_64).
In the project root folder:
wget https://xdebug.org/files/binaries/dbgpClient
chmod +x dbgpClient
./dbgpClient #OUTPUT
Xdebug Simple DBGp client (0.6.1)
Copyright 2019-2024 by Derick Rethans
Waiting for debug server to connect on port 9003.So if you haven’t already, start the built-in PHP server in a new command prompt:
php -S 127.0.0.1:8000The Xdebug output will change to:
#OUTPUT
Connect from 127.0.0.1:37386
DBGp/1.0: Xdebug 3.4.7 — For PHP 8.4.15
Debugging file:///home/fellipe/projects/symfony/my-clone-of-symfony-gs/index.php (ID: 294841/YOUR-NAME)
(cmd) If PHP/Xdebug run on a different machine, virtual host, or in a Docker container, you need to tell Xdebug where to make the debugging connection to.
Configuriing Xdebug to connect with a PHPStorm
./dbgpClient
Xdebug Simple DBGp client (0.6.1)
Copyright 2019-2024 by Derick Rethans
Waiting for debug server to connect on port 9003.